Disturbed sensory perception related to medically imposed restrictions (aneurysm precautions) Anxiety related to illness and/or medically imposed restrictions (aneurysm precautions) Nursing Diagnosis for Altered Level of ConsciousnessOct 19, 09 · Nursing Diagnosis for Hemorrhagic Stroke Ineffective tissue perfusion (cerebral) related to bleeding or vasospasm;• Assess neurological status and level of consciousness Potential Nursing Diagnoses • Injury, Risk for related to falls • Knowledge Deficient, related to drug action and side effects • Tissue perfusion, Ineffective related to decreased cardiac contractility • Nutrition more than body requirement, risk for imbalanced related to

Best Practice In Nursing Care Of Dyspnea The 6th Vital Sign In Individuals With Copd Semantic Scholar
Level of consciousness nursing diagnosis
Level of consciousness nursing diagnosis-Altered level of consciousness (ALOC) means that you are not as awake, alert, or able to understand or react as you are normally ALOC can be caused by a head injury, medicines, alcohol or drugs, dehydration, or some diseases, such as diabetes Different levels of ALOC includeTherapeutic Intervention / Medical Management Investigate changes in level of consciousness Rationale Changes in mentation may reflect hypoxemia and respiratory



Nursing Diagnosis For Copd Nursing Care Plan Interventions For Copd
Patients with diagnosis of acute drug poisoning admitted to Medical Toxicology Center (MTC) and general ICU of Imam Reza Hospital, Mashhad, Iran, were included The patients' consciousness level was assessed by the researchers (ARK and JT) upon their admission Patients younger than 18 years or older than 65 years were excluded In additionJul 23, 18 · When documenting your patient's level of consciousness, you'll notice you have a LOT of options to choose from Your patient can be alert, confused, in a coma and anything in between Knowing the difference between each level of consciousness will help you chart accurately and communicate your patient's condition with precisionNever Carry Dirty Socks Or Smelly Clothes NNormal CConfused DDelerious SSomnolent OObtunded SStuporous Comatose Description The different levels of consciousness that range from normal to comatose, in order
A child presenting with decreased level of conscious (dLOC) is of great concern due to the wide range of possible causes, and potential for death or serious longterm sequelae It is therefore vital that health professionals can recognise a child with dLOC quickly, intervene appropriately and escalate for senior review as a matter of urgencyMay 06, 15 · Nursing Diagnosis for Hemorrhagic Stroke Ineffective tissue perfusion (cerebral) related to bleeding or vasospasm;Disturbed sensory perception related to medically imposed restrictions (aneurysm precautions) Anxiety related to illness and/or medically imposed restrictions (aneurysm precautions) Nursing Diagnosis for Altered Level of Consciousness
Feb 11, 17 · CHAPTER 2 Selected Nursing Diagnoses, Interventions, Rationales, and Documentation Nursing Diagnosis ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx Definition Insufficient physiological or psychological energy to endure or complete required or desired daily activities CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Subjective Objective Verbal report of fatigue or weaknessAltered Level of Consciousness Validity of a Nursing Diagnosis Joan S RN, DSN, CS Author Information Assistant Professor University of Alabama School of Nursing UAB Station Birmingham, Alabama Journal of Neuroscience Nursing August 1990 Article Level Metrics Related Links Articles in PubMed by Joan S Grant, RN, DSN, CSThe purpose of this three‐phase study was to examine the validity of the nursing diagnosis altered level of consciousness (ALC) The conceptual framework was diagnostic reasoning



Deficient Fluid Volume Nursing Brain
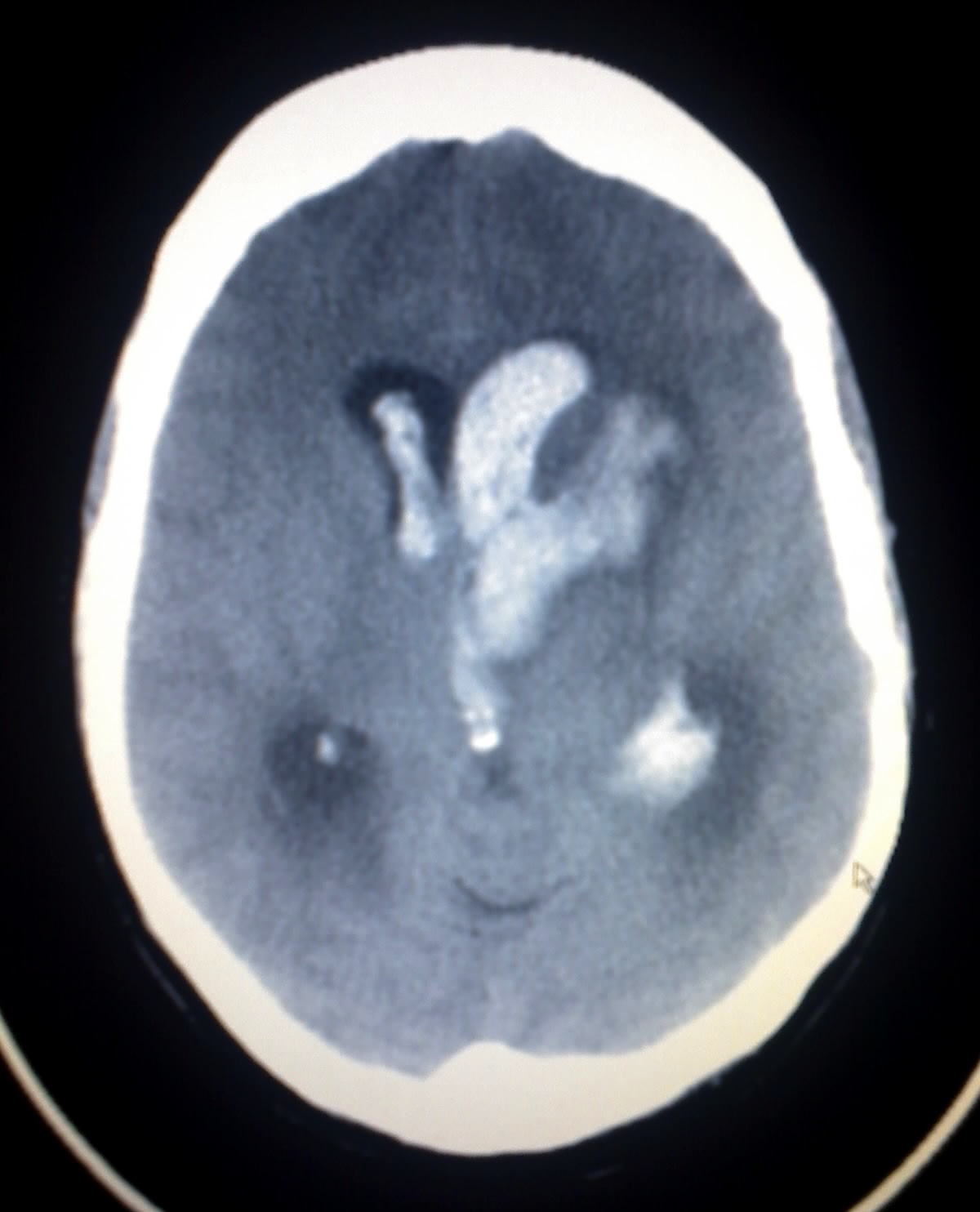


Altered Level Of Consciousness Wikipedia
May 12, 21 · Examples of nursing diagnoses that might fall under this first category include Ineffective airway clearance and Deficient fluid volume The second level is patient safety and security Examples of safety diagnoses that should be highly prioritized include Risk for injury and Risk for suffocationOct 18, 12 · Nursing Diagnosis• Ineffective airway clearance related to altered level of consciousness• Risk of injury related to decreased level of consciousness• Deficient fluid volume related to inability to take in fluids• Impaired oral mucous membranes related to mouth breathing, absence of pharyngeal reflex, and altered fluid intake•Level B Clinicians should attempt to increase arousal before performing evaluations to assess level of consciousness any time diminished arousal is observed or suspected Clinicians should identify and treat conditions that may confound accurate diagnosis of a DoC prior to establishing a final diagnosis



5 Impaired Gas Exchange Nursing Care Plans Nursestudy Net



Nursing Care Plan Of Hemophilia
Unfortunately, there is no classic presentation for a patient with AMS The terms, "Altered mental status" and "altered level of consciousness" (ALOC) are common acronyms, but are vague nondescript terms The same can be said about terms such as lethargy or obtundationMonitor level of consciousness A decreased level of consciousness is a prime risk factor for aspiration Assess cough and gag reflex A depressed cough or gag reflex increases the risk of aspiration Auscultate bowel sounds toObjective Vital signs T365, HR 165bpm, RR 45cpm, BP 90/60 mmHg HC 426cm (95th percentile) Physical Assessment Lethargic with decreasing level of consciousness Risk Question NCP CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION PLANNING IMPLEMENTATION SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION Subjective The mother thinks that her infant feels


View Of Nursing Diagnostics Results And Interventions To Elderly Patients With Diabetes A Case Study Online Brazilian Journal Of Nursing



Altered Level Of Consciousness
Oct 13, 14 · Nursing Diagnosis 1 Acute Confusion R/T Hyperammonemia secondary to Cirrhosis Encephalopathy results in moderate to severe confusion, lapses in memory, agitation and delayed reflexes These factors increase the risk for physical and psychosocial injury The effect is increased if patient has a history of alcohol or drug abuse, or if theJul 08, 08 · Consciousness is defined as the state of being aware of physical events or mental concepts Conscious patients are awake and responsive to their surroundings (Marcovitch, 05) The level of consciousness has been described as the degree of arousal and awareness A manifestation of altered consciousness implies an underlying brain dysfunctionThe level of consciousness determines to a certain extent the level of functional disturbance within the neuraxis A patient who qualifies as a grade I or II has cortical or diencephalic dysfunction The grade III patient has physiologic dysfunction above the midbrain Consequently, the history is important in the diagnosis of the causes of



Solved 39 Nursing Care Of Patients In Shock Chapter 9 3 Chegg Com


Key Nursing Interventions For Hyponatremia Patient
GCS (GLASGOW COMA SCALE) is a scale that is used to determine or assess the patient's level of consciousness, ranging from a fully conscious state to a state of coma On examination of consciousness or GCS, there are 3 functions (E, V, M) to be examined, each function has different values, for the following explanationNursing Diagnosis Intervetions Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia 1 Fluid Volume Deficit related to inadequate fluid intake, phototherapy, and diarrhea Goal Body fluids of neonates adequate Intervention Record the amount and quality of feces, skin turgor monitor, monitor intake output, give water between nursing or giving a bottle 2Jan 03, 15 · Primary Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume excess related to retention;


Nursing Diagnosis Android Apps Appagg



Pdf Nursing Care In Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Semantic Scholar
Risk for injury related to altered cerebral function, fluctuating levels of consciousness, disturbed orientation, and misperception ofSomeone in this state can be aroused with little difficulty People who are obtundedSep 01, 16 · Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Nursing Care Plans ACUTE CONFUSION Abrupt onset of a cluster of global, transient changes and disturbances in attention, cognition, psychomotor activity, level of consciousness, and/or sleep/wake cycle
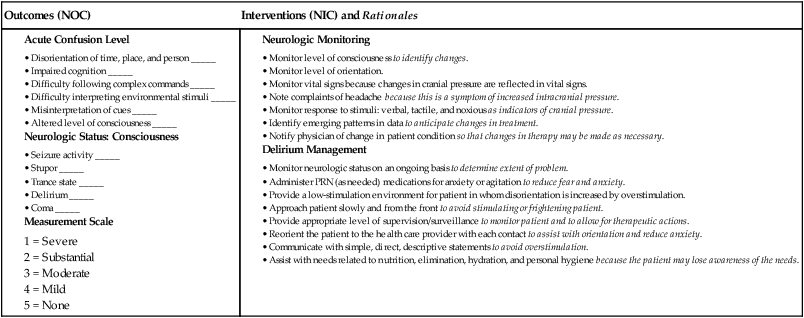


Nursing Management Acute Intracranial Problems Nurse Key



Imbalanced Nutrition Nursing Diagnosis For Newborn
Simple bedside assessment of level of consciousness comparison of two simple assessment scales with the Glasgow Coma scale* A F McNarry1 and D R Goldhill2 1 Research Registrar, 2 Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant in Anaesthesia and Critical Care Medicine, Department¾Describe the pathophysiology, management and nursing interventions of ¾Hydrocephalus ¾Cerebrovasculardisease ¾Meningitis ¾Seizures/status epilepticus ¾Head/Spinal Cord Injury ¾Neuromuscular Disorders Basic Neurologic Exam •Level of consciousness •GCS •Orientation and speech fluency •Cranial Nerves •Strength, driftAug 04, 17 · management of patients with altered level of consciousness altered level of consciousness mr anilkumar br msc nursing lecturer medicalsurgical nursing 2 ∗ The human brain requires a constant supply of oxygen and glucose for normal function ∗ Interruption of this supply will cause loss of consciousness within a few seconds and may also



Altered Level Of Consciousness



Please Give A Nurses Note In A Paragraph And Give Chegg Com
Nursing Care Plan for Unconsciousness Primary Assessment 1 Airway Does the patient speak and breathe freely There was a decrease of consciousness Abnormal breath sounds stridor, wheezing, wheezing, etc The use of a respirator muscles Restless Cyanosis Seizures Retention of mucus / sputum in the throat Hoarseness Cough 2 BreathingNeurological Altered Level of Consciousness (LOC) Level of responsiveness and consciousness is the most important indicator of the patient's condition LOC is a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition (consciousness) to coma Altered LOC is not the disorder but the result of a pathology Coma Unconsciousness, unarousable unresponsivenessALTERED LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS VALIDITY OF A NURSING DIAGNOSIS by Joan Staggs Grant, 19 edition,



Cancer Nursing Care Plan And Nanda Guidelines Updates



Post Surgery Care For Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Nursing Interventions Scientific Rationale;Mar 06, 21 · A nurse who is caring for an unresponsive client formulates the nursing diagnosis, "Risk for Aspiration related to reduced level of consciousness" The nurse documents this nursing diagnosis as correct based on the understanding that which of the following is a characteristic of this type of diagnosis?Apr 30, 14 · What is altered level of consciousness?



Fever Nursing Care Plan Fever Medicine



Nursing Care Plan Breathing Respiratory Tract
Skilled nursing assessment of altered level of consciousness leads to early nursing and medical intervention, which, in turn, can improve patient outcomes In this paper, a critical review of the literature will focus on altered level of consciousness inThe purpose of this three‐phase study was to examine the validity of the nursing diagnosis altered level of consciousness (ALC) The conceptual framework was diagnostic reasoningAssessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Obtain a complete health history including allergies, drug history, and possible drug interactions Assess pain (quality, intensity, location, duration) and effect on sleep pattern Assess respiratory function Assess level of consciousness before and after administration Obtain vital signs



Nanda International Nursing Diagnosis List 21 Public Health



Caring For Patients With Lumbar Drains American Nurse
What is the priority nursing diagnosis for a patient with fluctuating levels of consciousness, disturbed orientation, and visual and tactile hallucinations?An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment A mildly depressed level of consciousness or alertness may be classed as lethargy;Concept analysis is the first step in instrument development Steps in the concept analysis process are discussed and applied to the analysis of altered level of consciousness (ALC) as a potential nursing diagnosis for submission to the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association



Comprehensive Overview Of Nursing And Interdisciplinary Care Of The Acute Ischemic Stroke Patient Stroke



Abc S Of Medical And Surgical Nursing Gastric Carcinoma Surgical Nursing Nursing Diagnosis
NURSING DIAGNOSES Ineffective airway clearance related to altered LOC GOALS To maintain a patent airway and ensure ventilation EXPECTED OUTCOME Maintains clear airway and demonstrates appropriate breath sounds Nursing Diagnoses for pt with altered level of consciousness Uploaded by mikaela_pascua 94% (35) 94% found this document usefulIs written as a twopart statementJul 19, 12 · Diagnosis and treatment of decreased consciousness begins with a complete medical history and physical examination, which includes a detailed neurological evaluation Your doctor will want to know



Nursing Diagnosis For Copd Nursing Care Plan Interventions For Copd



Altered Consciousness In Pediatrics Aeioutips Movestupid
Jul 09, · Ryan Barnett Nursing Care Plan Risk For Injury Assessment Diagnosis Plan Goals/Outcomes Interventions Nursing Orders Rationale Evaluation client who has bipolar disorder Risk For Injury r/t bipolar disorder Goal Pt maintains usual level of consciousness q shiftLevels of consciousness 1 Nursing Diagnosis According to Priority 1 Ineffective airway clearance related to upper airway obstruction, by tongue and soft tissues, inability to clear respiratory secretions as evidenced by unclear lung sounds, unequal lung expansion, noisy respiration, presence of stridor, cyanosis or pallor



Abc S Of Medical And Surgical Nursing Raynaud S Disease Surgical Nursing Nursing Diagnosis



Concussion Diagnosis And Treatment Nursing Ce Course Nursingce
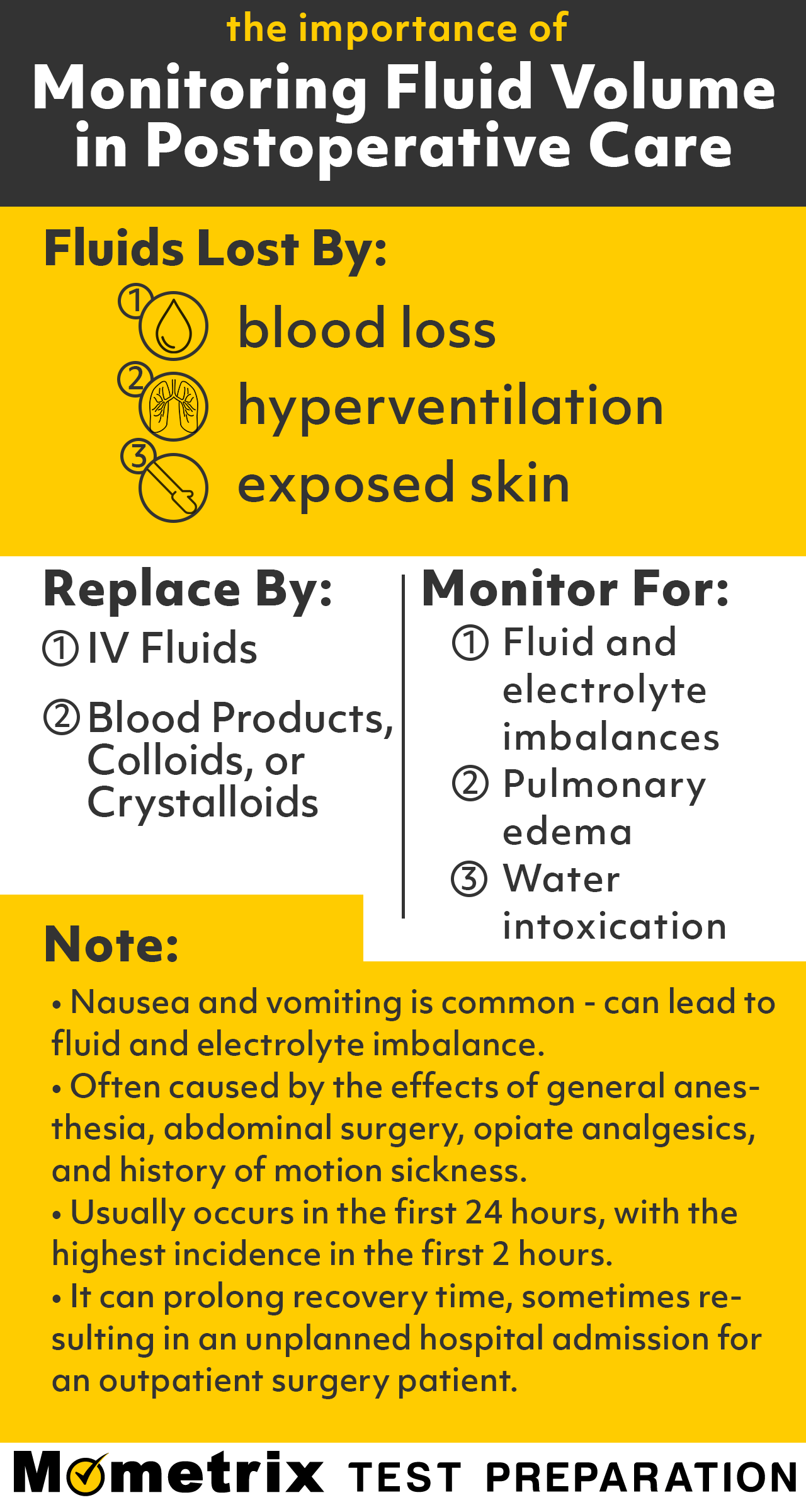


An Overview Of Postoperative Care Nursing Review Video



Acute Confusion Nursing Brain



Nursing Care Of The Surgical Patient Straight A Nursing



Best Practice In Nursing Care Of Dyspnea The 6th Vital Sign In Individuals With Copd Semantic Scholar



Activity Intolerance Nursing Care Plan Nanda Nursing Diagnosis



Please Give A Nurses Note In A Paragraph And Give Chegg Com


Clinical Guidelines Nursing Observation And Continuous Monitoring



Decreased Level Of Consciousness In A Child Recognition And Management British Journal Of Nursing
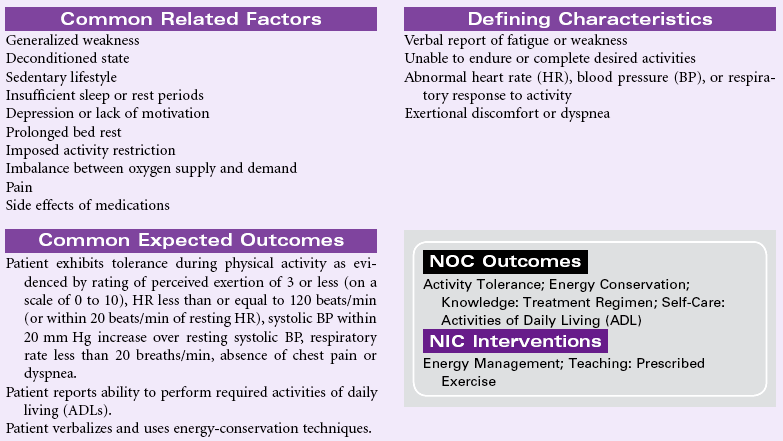


Nursing Diagnosis Care Plans Nurse Key



7 Meningitis Nursing Care Plans Nurseslabs



Decreased Level Of Consciousness In A Child Recognition And Management British Journal Of Nursing
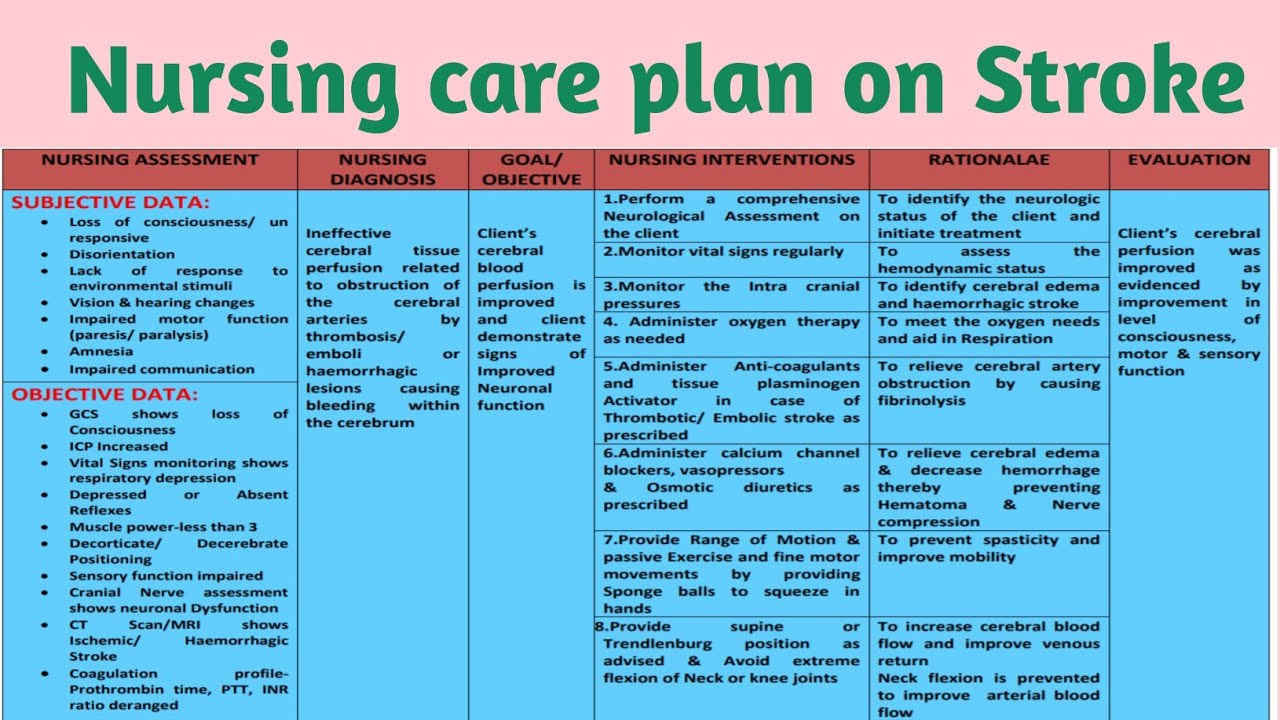


Ncp 4 Nursing Care Plan For A Stroke Patient Cerebrovascular Accident Cva Youtube


Unconscious Clients Patients Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Procedure



Nursing Diagnoses For Pt With Altered Level Of Consciousness Zpnx5p7e8e4v
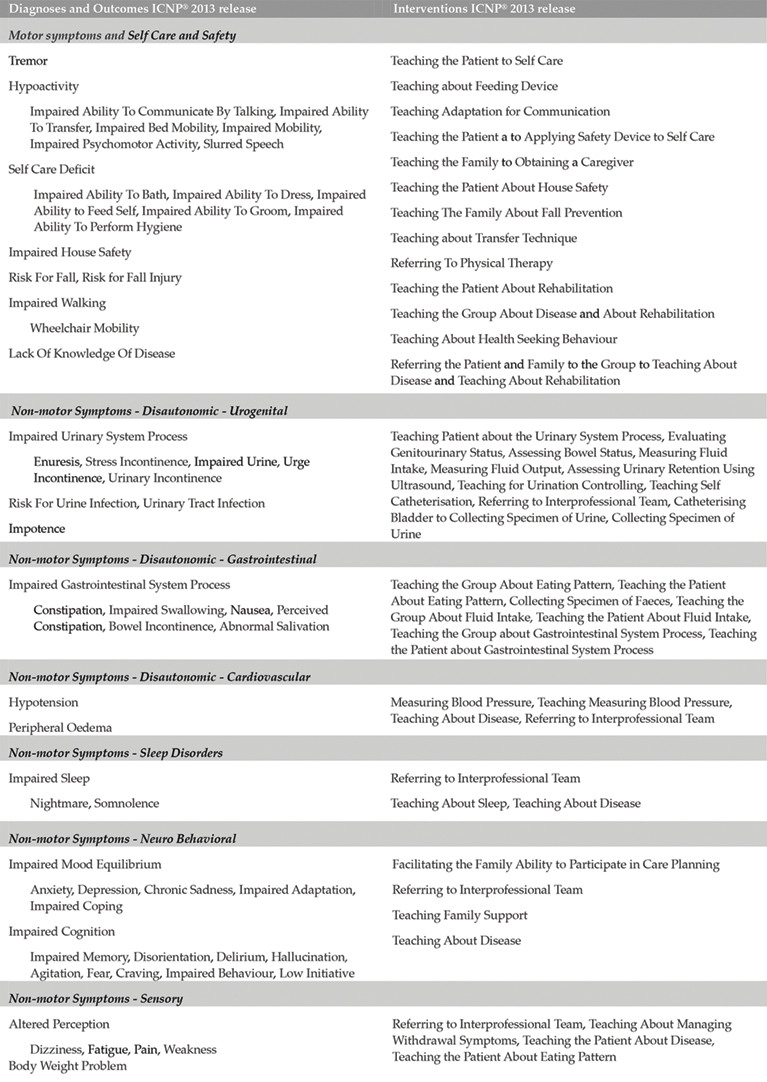


The Role Of Nurses In Parkinson S Disease Intechopen



Nursing Diagnosis Everything You Need To Know Guide Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plan Nursing Care



Clinical Decision Making The Nursing Process Nrs 110 Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Critical Thinking Revisited Knowledge Experience Reflection Intuition Components Of Critic


Nursing Process The Patient With An Altered Level Of Consciousness



Nursing Care Plan Epidural Hematoma Post Craniotomy



Perioperative Nursing Care Ppt Video Online Download



Ncp Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Stroke Neurology



Acute Confusion Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan Nurseslabs



Sleep Apnea Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions Nursestudy Net



Nursing Care Plan 1 Alcohol Detox Doc Nursing Care Plan Form Student Name Michelle Margarucci Patient Identifier A D Date Patient Medical Diagnosis Course Hero



Altered Loc And Brain Death Objectives Studocu



Nursing Diagnosis List Nanda Nursing Diagnosis List



Nursing Diagnosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Management Of Patients With Neurological Disorders Ppt Download



Respiratory Failure Nursing Care Plan Rnspeak



Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan For Syncope Fainting Nursing Com


Application Of The Nursing Process Delirium


Proposal Of Nursing Care Plan In People Hospitalized With Aids



Key Nursing Interventions For Hyponatremia Patient



Nursing Care Plans Hypovolemic Shock Studocu


Cuidados Integrales De Enfermeria En Un Lactante Con Encefalopatia Isquemica Hipoxica Relacionada Con La Asfixia Perinatal



Nursing Diagnosis List Neurological Disorders From The Nursing Station



Fever Nursing Care Plan Mwl1vrv9w5lj



Pin On Ncp



Ppt Chapter 61 Management Of Patients With Neurologic Dysfunction Powerpoint Presentation Id


Nursing Diagnosis List Nanda Nursing Diagnosis List
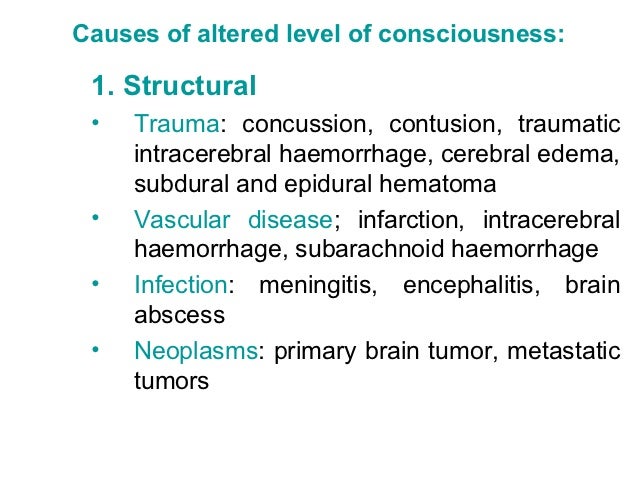


Altered Level Of Consciousness



Nursing Diagnosis For Copd Nursing Care Plan Interventions For Copd



6 Success Steps For Diagnosing Altered Level Of Consciousness



Hyperkalemia Recognition And Management Of A Critical Electrolyte Disturbance Article Nursingcenter



Dystocia Nursing Care Plans And Diagnosis Interventions Nursestudy Net


View Of Nursing Diagnostics Results And Interventions To Elderly Patients With Diabetes A Case Study Online Brazilian Journal Of Nursing


Precautions When Caring For Patient With Levels Of Consciousness



Using The Ability Model To Design And Implement A Patient Care Plan The Veterinary Nurse



Pdf Nursing Diagnosis Outcomes And Interventions For Critically Ill Patients Affected By Covid 19 And Sepsis
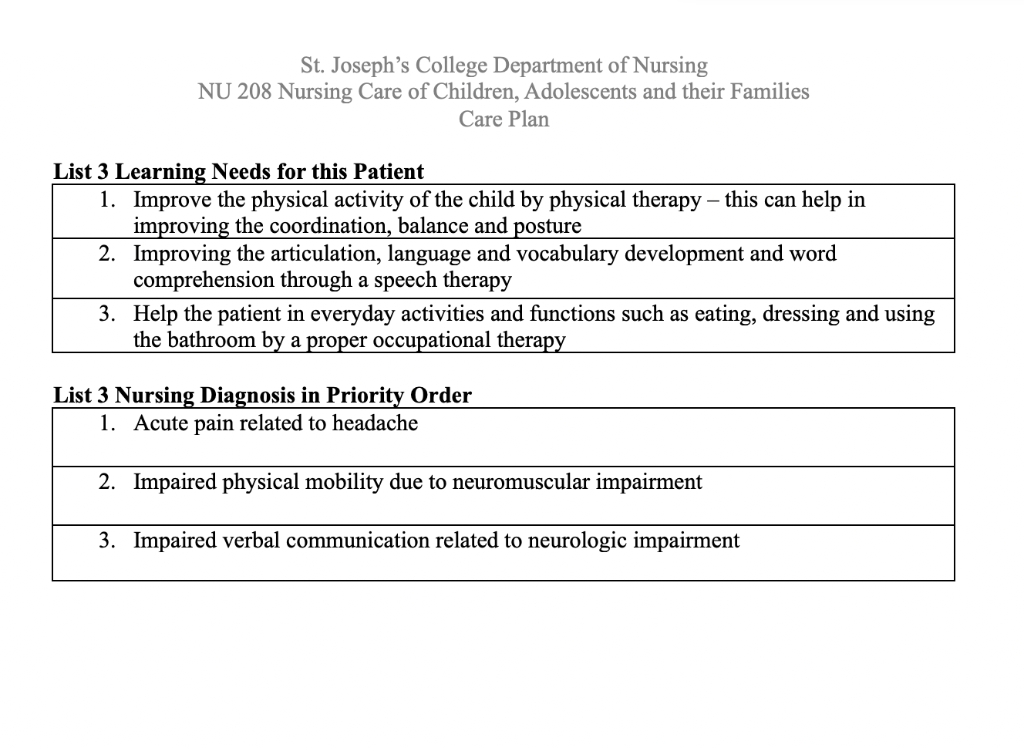


Please Give A Nurses Note In A Paragraph And Give Chegg Com
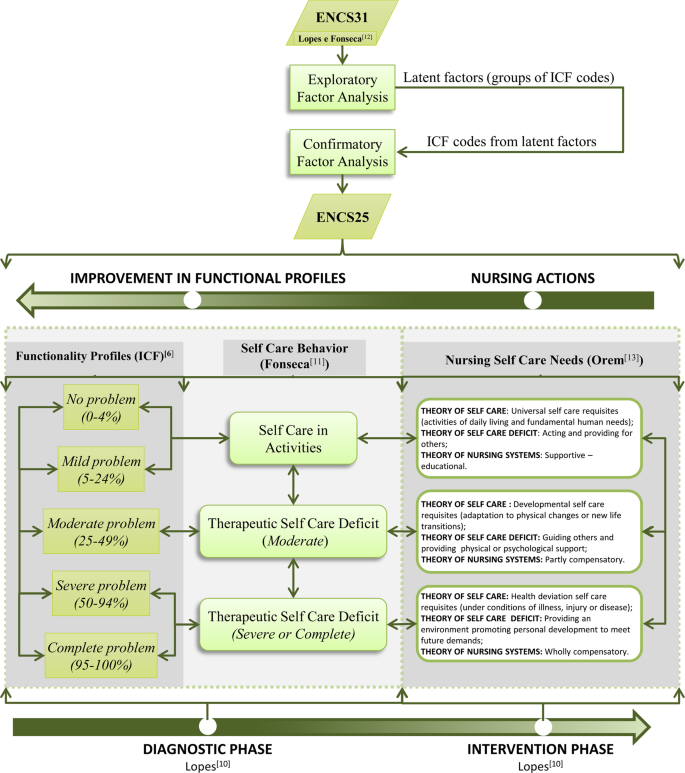


A Nursing Care Intervention Model For Elderly People To Ascertain General Profiles Of Functionality And Self Care Needs Scientific Reports



Altered Level Of Consciousness
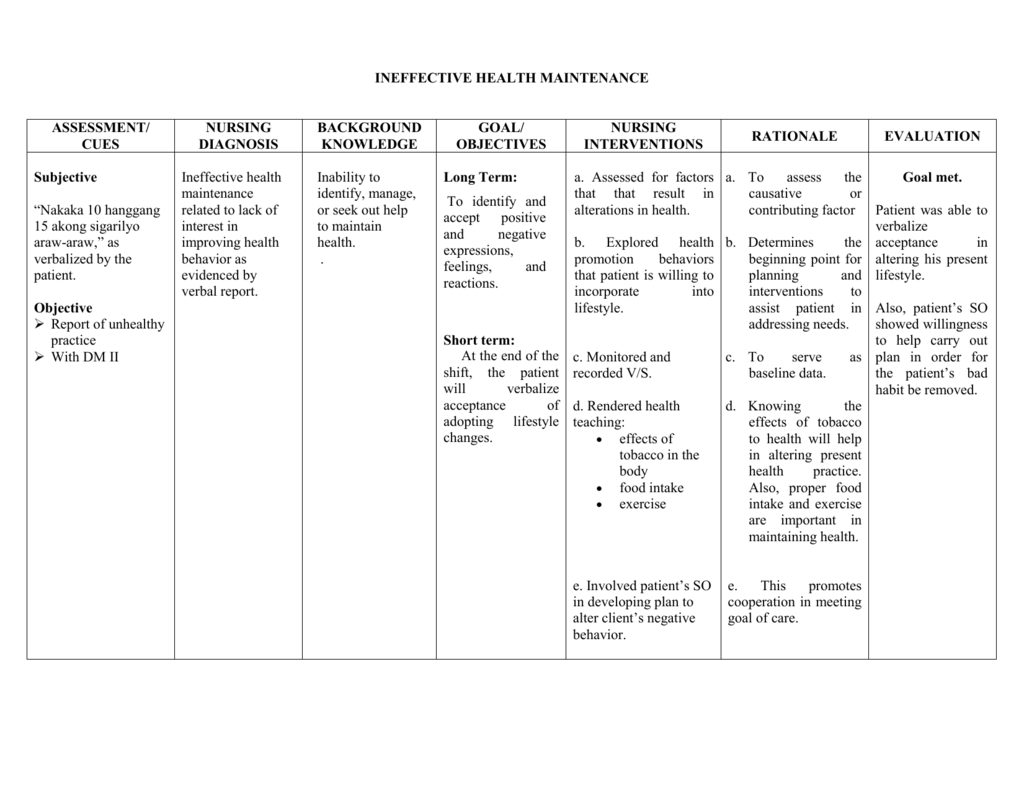


Alteration In Health Maintenance
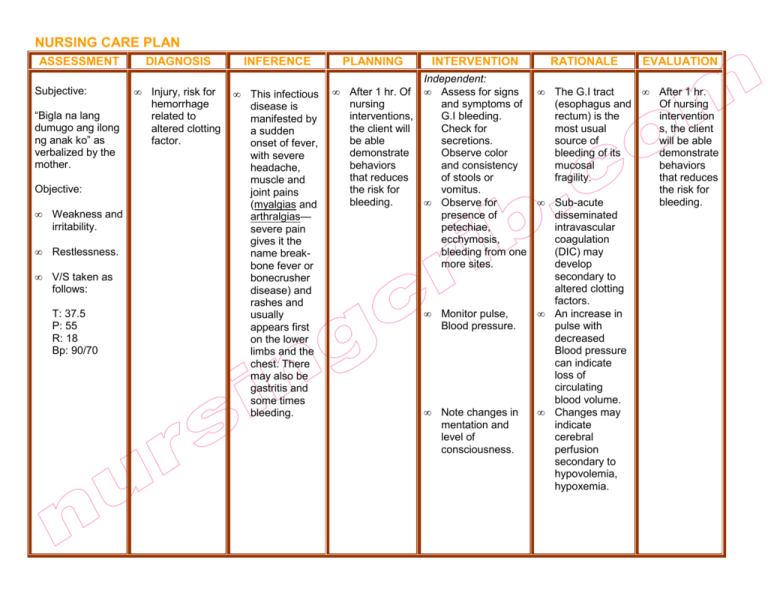


Nursing Care Plan Dengue



Altered Level Of Consciousness



Pdf Nursing Care In Severe Traumatic Brain Injury



Ineffective Breathing Pattern Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan Rnlessons



Ncp For Altered Conciousness Coma Liver



Management Of Clients With Altered Level Of Consciousness



Nursing Diagnoses For Pt With Altered Level Of Consciousness Urinary Incontinence Clinical Medicine


Unconscious Clients Nursing Care Plan
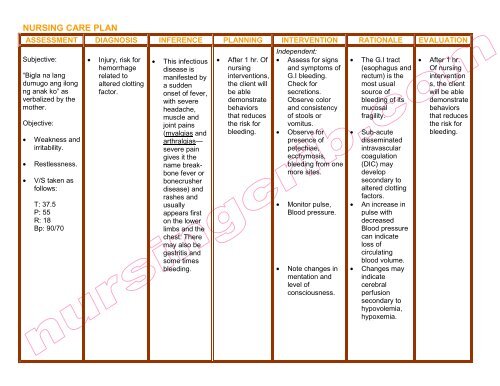


Nursing Care Plan Dengue Nursing Crib



Unit Ii Common Signs Symptoms Topic Electrolyte Imbalanceshyponatremia



12 Stroke Cva Nursing Diagnosis And Nursing Care Plans Nurseslabs



Altered Level Of Consciousness



13 Neurocognitive Disorders Nurse Key
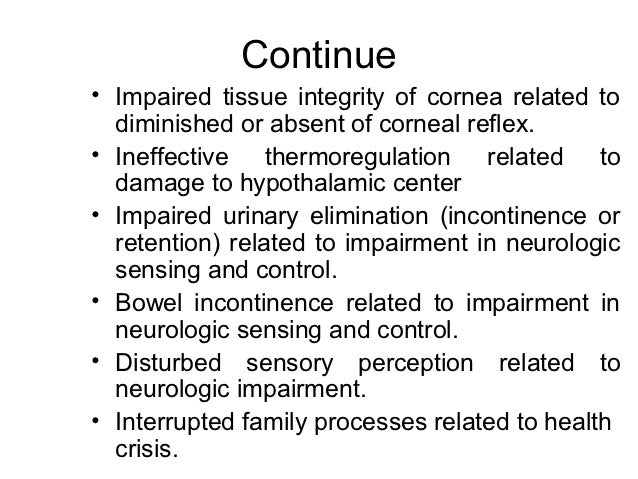


Altered Level Of Consciousness


Management Treatment Case Study 9 Blunt Abdominal Trauma Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
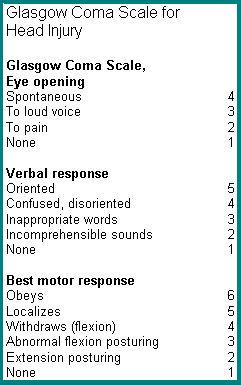


Nursing Diagnoses Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head Injury



57 Year Old Female Admitted To The Hospital With Complaints Complaints Of Sob And Copd Exacerbation



No comments:
Post a Comment